# matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.style
#ggplotを使用する
matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
# MATLABスタイル
matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
x = [0,1,2,3,4]
y = [0,1,2,4,8]
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.title('MATLAB-STYLE')
Text(0.5,1,'MATLAB-STYLE')
# オブジェクト指向スタイル
x = [0,1,2,3,4]
y = [0,1,2,4,8]
#スタイルの指定は matplotlib.style.available で確認できる
matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
# 2行2列のプロットを用意する
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2,ncols=2)
# 1行1列にプロットする
axes[0,0].plot(x, y, label='legend_001')
axes[0,0].legend(loc='best') # 凡例 外配置は loc='bbox_to_anchor'
# 個別のグラフ axes を装飾する
axes[0,0].set_title('axes[0,0].set_title') # タイトル
axes[0,0].set_xlabel('axes[0,0].set_xlabel') # x軸ラベル
axes[0,0].set_ylabel('axes[0,0].set_ylabel') # y軸ラベル
# 全体 fig を装飾する
fig.suptitle('fig.suptitle')
# グラフを保存する
fig.savefig('data/savefig.png')
# グラフを表示する
plt.show()
# 縦棒グラフ ax.bar
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2)
matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
x = [0,1,2]
y = [2,4,5]
# x軸ラベルを任意のラベルにする
labels = ['label_0','label_1','label_2']
axes[0].bar(x, y, tick_label=labels)
plt.show()
# 横棒グラフ ax.barh
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2)
matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
x = [0,1,2]
y = [2,4,5]
# x軸ラベルを任意のラベルにする
labels = ['label_0','label_1','label_2']
axes[0].barh(x, y, tick_label=labels)
plt.show()
# 縦棒グラフ 2本並べる ax.bar
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2)
matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
x1 = [0,1,2]
y1 = [2,4,5]
y2 = [3,5,7]
# x軸ラベルを任意のラベルにする
labels = ['label_0','label_1','label_2']
# 棒の幅を決める y1
width = 0.4
axes[0].bar(x1, y1, tick_label=labels, width=width, label='y1')
axes[0].legend(loc='best')
# 棒の幅の分をx軸の正方向にずれた位置に y2 の棒グラフを書く
x2 = [i + width for i in x1]
axes[0].bar(x2, y2, tick_label=labels, width=width, label='y2')
axes[0].legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
# 積み上げ棒グラフ
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,2)
matplotlib.style.use('ggplot')
x = [0,1,2]
y1 = [2,4,5]
y2 = [3,5,7]
# x軸ラベルを任意のラベルにする
labels = ['label_0','label_1','label_2']
# y1とy2 を足した y_total = y1 + y2 を作成する
y_total = [i + j for i, j in zip(y1, y2)]
# y_total の上に y2 で塗りつぶし、残りの部分を y1 と見立てる
axes[0].bar(x,y_total, tick_label=labels, label='y1')
axes[0].legend(loc='best')
axes[0].bar(x,y2, tick_label=labels, label='y2')
axes[0].legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
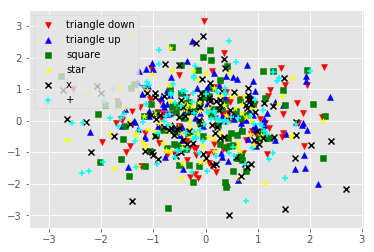
# 散布図
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# ランダム値を生成
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
# 各種マーカーを使用してみる
ax.scatter(x[0:100], y[0:100], marker='v', label='triangle down', color='red')
ax.scatter(x[100:200], y[100:200], marker='^', label='triangle up', color='blue')
ax.scatter(x[200:300], y[200:300], marker='s', label='square', color='green')
ax.scatter(x[300:400], y[300:400], marker='*', label='star', color='yellow')
ax.scatter(x[400:500], y[400:500], marker='x', label='x', color='black')
ax.scatter(x[500:600], y[500:600], marker='+', label='+', color='cyan')
plt.legend(loc='best')
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x176cffce710>
# ヒストグラム
np.random.seed(1)
ave = 100
std = 15
x = np.random.normal(ave, std, 1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
n, bins, patches = ax.hist(x, bins=20)
plt.show()
n # 各棒の度数
bins # 各棒の境界値
patches # 各棒の描画情報
<a list of 20 Patch objects>
# ヒストグラム 横棒
np.random.seed(1)
ave = 100
std = 15
x = np.random.normal(ave, std, 1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
n, bins, patches = ax.hist(x, bins=20, orientation='horizontal')
plt.show()
# ヒストグラムを並べる
np.random.seed(2)
# 正規分布に従うデータを3つ用意する
x0 = np.random.normal(10,10,1000)
x1 = np.random.normal(10,20,1000)
x2 = np.random.normal(10,30,1000)
# ヒストグラムを書く
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
labels = ['x0', 'x1', 'x2']
ax.hist([x0,x1,x2],label=labels)
plt.legend(loc='best')
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x176bad74470>
# ヒストグラムを積み上げる
np.random.seed(2)
# 正規分布に従うデータを3つ用意する
x0 = np.random.normal(10,10,1000)
x1 = np.random.normal(10,20,1000)
x2 = np.random.normal(10,30,1000)
# ヒストグラムを書く
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
labels = ['x0', 'x1', 'x2']
ax.hist([x0,x1,x2],label=labels, stacked=True)
plt.legend(loc='best')
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x176cfeeeef0>
# 箱ひげ図 .boxplot
# 正規分布に従うデータを3つ用意する
np.random.seed(0)
x0 = np.random.normal(10,10,1000)
x1 = np.random.normal(10,20,1000)
x2 = np.random.normal(10,30,1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
labels = ['x0', 'x1', 'x2']
ax.boxplot([x0,x1,x2], labels=labels)
plt.show()
# 箱ひげ図.boxplot(横向き vert=False)
# 正規分布に従うデータを3つ用意する
np.random.seed(0)
x0 = np.random.normal(10,10,1000)
x1 = np.random.normal(10,20,1000)
x2 = np.random.normal(10,30,1000)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
labels = ['x0', 'x1', 'x2']
ax.boxplot([x0,x1,x2], labels=labels, vert=False)
plt.show()
# 円グラフ ちょっと斜め上から
x = [3,5,7]
labels = labels = ['x0', 'x1', 'x2']
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.pie(x, labels=labels)
plt.show()
# 円グラフ 真上から ax.axis('equal')
x = [3,5,7]
labels = labels = ['x0', 'x1', 'x2']
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.pie(x, labels=labels )
ax.axis('equal') # 真上から
plt.show()
# 円グラフ 真上から ax.axis('equal')
# 12時(startangle=90) から 時計回り(counterclock=False) で
# 影をつける shadow=True
# %を入れる autopct='%1.2f%%'
# 一部を切り離す explode
x = [3,5,7]
labels = labels = ['x0', 'x1', 'x2']
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
explode =[0,0.1,0] # 2番めのデータだけ切り離す
ax.pie(x, labels=labels, startangle=90, counterclock=False, shadow=True, autopct='%1.2f%%', explode=explode)
ax.axis('equal')
plt.show()
# グラフを組み合わせる 棒グラフ-折れ線グラフ
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x1 = [0,1,2,3]
y1 = [1,3,5,7]
x2 = [0,1,2,3]
y2 = [10,8,20,10]
ax.bar(x1, y1, label='y1') # 棒グラフ ax.bar()
ax.plot(x2, y2, label='y2') # 折れ線グラフ ax.plot()
ax.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
# グラフを組み合わせる ヒストグラム-折れ線グラフ
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# サンプルデータを生成する
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.random.randn(1000)
# ヒストグラムを描く
counts, edges, patches = ax.hist(x, bins=30)
#中点を求める(何故かこれで求まるらしい)
x_fit = (edges[:-1] + edges[1:])/ 2
y=1000 * np.diff(edges) *np.exp(-x_fit**2 / 2)
np.sqrt(2 * np.pi)
ax.plot(x_fit, y)
plt.show()
counts
# array([ 9., 20., 70., 146., 217., 239., 160., 86., 38., 15.])
edges
# array([-3.04614305, -2.46559324, -1.88504342, -1.3044936 , -0.72394379,
# -0.14339397, 0.43715585, 1.01770566, 1.59825548, 2.1788053 ,
# 2.75935511])
array([-3.04614305, -2.46559324, -1.88504342, -1.3044936 , -0.72394379,
-0.14339397, 0.43715585, 1.01770566, 1.59825548, 2.1788053 ,
2.75935511])
edges[1:]
array([-2.46559324, -1.88504342, -1.3044936 , -0.72394379, -0.14339397,
0.43715585, 1.01770566, 1.59825548, 2.1788053 , 2.75935511])
edges[:-1]
array([-3.04614305, -2.46559324, -1.88504342, -1.3044936 , -0.72394379,
-0.14339397, 0.43715585, 1.01770566, 1.59825548, 2.1788053 ])
# スタイル
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# 色 color=名称'red' 16進数RGB'#0000FF' RGBAをfloatで
ax.plot([0,1], [1,1], color='red')
ax.plot([0,1], [2,2], color='#0000FF')
ax.plot([0,1], [3,3], color=[0.2, 1.0, 0.2, 1.0])
plt.show()
# 色 color=名称'red' 16進数RGB'#0000FF' RGBAをfloatで
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# 棒グラフは color と edgecolor を設定できる
ax.bar([1], [3], color='red')
ax.bar([2], [4], color='cyan' , edgecolor='black')
plt.show()
# 線のスタイル 幅linewidth ラインスタイルlinestyle
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([0,1], [0,0])
ax.plot([0,1], [1,1], linewidth=1 ,linestyle='--')
ax.plot([0,1], [2,2], linewidth=5 ,linestyle='-.')
ax.plot([0,1], [3,3], linewidth=10 ,linestyle=':')
plt.show()
# フォント family, size, weght
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_title('set_title', family='fantasy', size=20, weight='bold')
ax.set_xlabel('set_xlabel', family='DejaVu Sans', size=30, weight='light')
ax.set_ylabel('set_ylabel', family='monospace', size=25, weight='heavy')
plt.show()
# フォントはまとめてディクショナリにできる
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
fontdict = {
'family': 'fantasy',
'size': 20,
'weight': 'normal',
}
ax.set_title('set_title', fontdict=fontdict, size=40)
ax.set_xlabel('set_xlabel', fontdict=fontdict)
ax.set_ylabel('set_ylabel', fontdict=fontdict)
plt.show()
# グラフにテキストを描く
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.text( 0, 0, 'text', size=10)
ax.text(0.2, 0.2, 'text', size=20)
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, 'text', size=30)
ax.text(1.0, 1.0, 'text', size=40)
plt.show()
# ---- end of scripts ----